
- Tyrosine melanin dopamine drawit update#
- Tyrosine melanin dopamine drawit skin#
- Tyrosine melanin dopamine drawit free#
Riederer, in Encyclopedia of Movement Disorders, 2010 Characteristics of Melanin and Neuromelanin (NM) – Similarity and Dissimilarity Vitiligo provides a model which demonstrates that Ayurveda has a richer view of its presentations, possibly a stronger line on its pathogenesis, and a huge range of herbals, many now backed by studies from ethnobotanical laboratories, awaiting research into the many possible mechanisms by which they may act in the wide and complex field of melanocyte biochemistry.M. Management that is inclusive of a maximally holistic approach justifies the use of diverse herbals, yoga and concern for cultural awareness provided by integrated medicine. There are other roles, biochemical and mechanical, of melanocyte. These important properties acquired a genetic basis much later than other functions, many relating to cell contact as in the keratinocyte -melanocyte unit, or as with the synapses of the neurological system.
Tyrosine melanin dopamine drawit skin#
Biomedicine emphasizes the role of melanocyte for protection from UV rays and as a determinant of skin colour.
Tyrosine melanin dopamine drawit update#
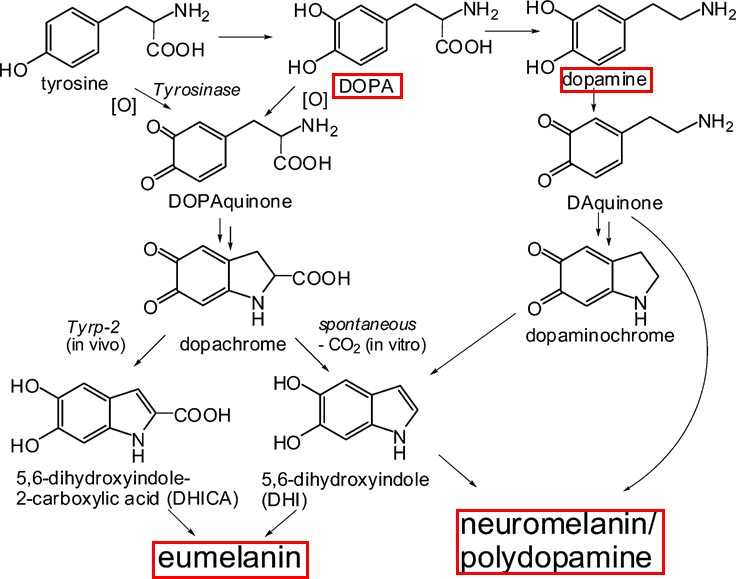
Here we update the neuroendocrine functions of melanocytes and discuss the possible involvement of melanocytes in the control of the central chemosensor that generates respiratory rhythm.heme hypoxia lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase melanocyte microphthalmia-associated transcription factorīiomedicine has not provided a complete explanation with fully effective therapies for disorders of pigmentation. Thus, melanocytes may exert hitherto unknown functions through L-PGDS and prostaglandin D 2. L-PGDS generates prostaglandin D 2 and also functions as an inter-cellular carrier protein for lipophilic ligands, such as bilirubin and thyroid hormones. More recently, we have shown that lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase (L-PGDS) is expressed in melanocytes but not in other skin cell types. Melanocytes therefore have attracted much attention of many ladies, makeup artists and molecular biologists. Sun tanning, melasma, aging spots (lentigo senilis), hair graying, and melanoma are well-known melanocyte-related pathologies. Moreover, heterozygous mutations in the gene coding for microphthalmia-associated transcription factor, a key regulator for melanocyte development, are associated with Waardenburg syndrome type 2, an auditory-pigmentary disorder. Impairment at each step causes the pigmentary disorders in humans, with the historical example of oculocutaneous albinism. The differentiation and functions of melanocytes are regulated at multiple processes, including transcription, RNA editing, melanin synthesis, and the transport of melanosomes to keratinocytes. Melanin pigment in the skin is produced by melanocytes under the influence of various endogenous factors, derived from neighboring keratinocytes and underlying fibroblasts. Melanocytes of neural crest origin are located in the skin, eye, inner ear, and leptomeninges. The skin is armored with "dead cells", the stratum corneum, and is continuously exposed to external stressful environments, such as atmospheric oxygen, solar radiations, and thermal and chemical insults. Furthermore, the resulting melanic component serves an additional protective role through its ability to chelate and accumulate metals, including environmentally toxic metals such as mercury and lead.lipids ͉ neuromelanin ͉ brain aging ͉ neurodegenerative The synthesis of neuromelanins in the various regions of the human brain is an important protective process because the melanic component is generated through the removal of reactive/toxic quinones that would otherwise cause neurotoxicity. The precursors of lipid components of the neuromelanins are the polyunsaturated lipids present in the surrounding organelles. These neuronal pigments have some structural similarities to the melanin found in skin. This contrasts with neuromelanin of the substantia nigra, where the melanic precursor is cysteinyl-dopamine.
Tyrosine melanin dopamine drawit free#
The melanic component is aromatic in structure, contains a stable free radical, and is synthesized from the precursor molecule cysteinyl-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine. These pigments, which we term neuromelanins, contain melanic, lipid, and peptide components. These pigments consist of granules 30 nm in size, contained in organelles together with lipid droplets, and they accumulate in aging, reaching concentrations as high as 1.5-2.6 g/mg tissue in major brain regions.
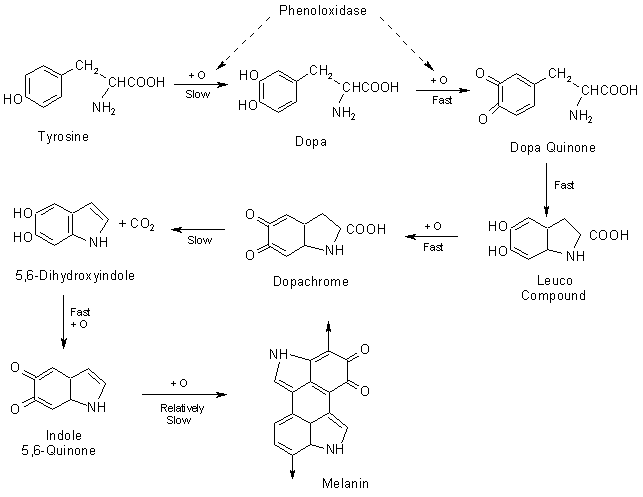
Neuronal pigments of melanic type were identified in the putamen, cortex, cerebellum, and other major regions of human brain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
